Economist A.C. Pigou argued that to deal with a negative externality in production, the government should impose a tax equal to the cost of the externality
What did Pigou believe should be done in the case of a positive externality in consumption? How would his recommendation impact the demand and market equilibrium for the product which is generating the positive externality?
Pigou believed that, in the case of a positive externality in consumption, the government should give consumers a subsidy equal to the value of the externality. By giving a subsidy equal to the value of the externality, the external benefit will become a private benefit and demand for the product will increase to the point where the market equilibrium is also the efficient equilibrium.
You might also like to view...
Which is NOT an example of moral hazard
a. people eat more at all-you-can-eat buffets b. loggers clear-cut a tract of land rather than when paying per tree felled c. Drivers of heavier, safer cares are more likely to run stop signs d. workers paid an hourly wage work harder than those on commission
________ is maximized when the marginal cost of production equals the marginal benefit to consumers
a. Efficiency b. Productivity c. Social welfare d. Economic profit
Based on this graph, the multiplier effect shifts the aggregate demand curve from ______.
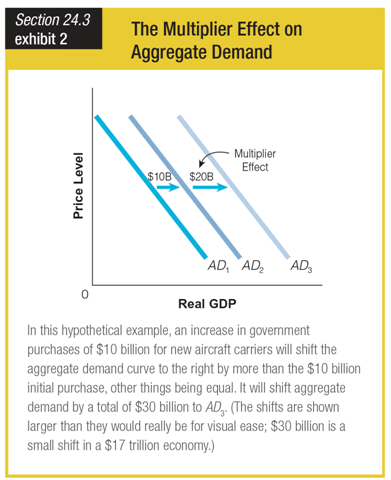
a. AD1 to AD2
b. AD2 to AD1
c. AD2 to AD3
d. AD1 to AD1
With ________, outcomes of specific interventions are determined by using the intervention in a randomly selected subset of a sample and then comparing outcomes from the exposed and control group.
A. natural experiments B. manipulated experiments C. random experiments D. predetermined experiments