In a single-price monopoly market
a. total benefit (the sum of consumer and producer surplus) is as large as it can possibly be
b. price and output are higher than they would be in an otherwise similar perfectly competitive market
c. price and output are lower than they would be in an otherwise similar perfectly competitive market
d. the quantity produced is artificially low, thereby creating an inefficiency
e. the price charged is artificially low, thereby creating an inefficiency
D
You might also like to view...
In a market, social surplus is maximized if consumers' willingness to pay for the good equals the ________
A) marginal private cost of producing the good B) marginal external cost of producing the good C) marginal social cost of producing the good D) opportunity cost of producing the good
Which of the following grew rapidly after the passage of the Medicare and Medicaid programs in the mid-1960s?
a. the share of healthcare expenditures financed directly by the consumer b. the share of healthcare expenditures financed by third parties c. the prices of healthcare relative to the prices of other goods and services d. both b and c
A monopolist maximizes profits by
a. producing an output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. b. charging a price equal to marginal revenue and marginal cost. c. charging a price where marginal cost equals average total cost. d. Both a and b are correct.
In an open economy, the quantity demanded of corn in the domestic market is ________.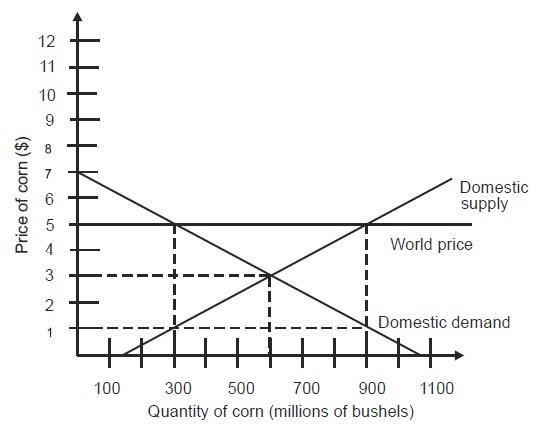
A. 150 million bushels B. 900 million bushels C. 300 million bushels D. 600 million bushels