Open-market operations, changes in reserve requirements, changes in the discount rate, and changes in the interest rate on reserves are known as
A) goals.
B) intermediate targets.
C) instruments.
D) derivatives.
C
You might also like to view...
In the fooling model's AD/SAS/LAS diagram, short-run equilibria to the right of the LAS curve require the price level to be
A) above what workers expect. B) above what firms expect. C) below what workers expect. D) below what firms expect.
If a manager of a firm believes one of their firm's suppliers is engaged in cartel activity, the manager ________ an incentive to report the behavior because they can ________.
A) has; have to pay whistle -blower fees B) does not have; receive treble damages C) has; receive treble damages D) does not have; have to pay whistle-blower fees
Although there are many reasons why a market can be non-competitive, the principal economic difference between a competitive and a non-competitive market is:
A) the number of firms in the market. B) the extent to which any firm can influence the price of the product. C) the size of the firms in the market. D) the annual sales made by the largest firms in the market. E) the presence of government intervention.
From the graph given, locate two points on an individual demand curve that you sketch directly below the graph presented 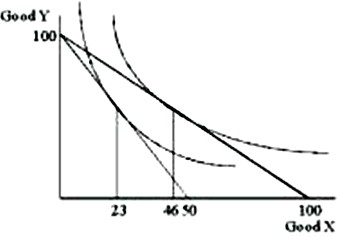
What will be an ideal response?