In this economic growth and production possibilities curve, what does point F represent compared to point B?
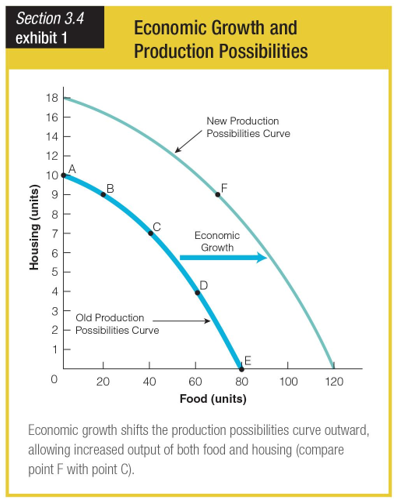
a. more housing units but the same number of food units
b. more housing units and more food units
c. more food units but the same number of housing units
d. the elimination of scarcity in housing and food
c. more food units but the same number of housing units
You might also like to view...
The two economists associated with the development of the theory of monopolistic competition were
A) Joan Robinson and Edward Chamberlin. B) David Hume and Adam Smith. C) John Neville Keynes and John Maynard Keynes. D) Carl Menger and Eugen Von Bohm-Bawerk.
Which of the following is likely to be an effect of inflation?
a. An increase in the willingness of lenders to lend money for longer periods b. A decrease in the willingness of borrowers to borrow money for longer periods c. A decrease in the purchasing power of lenders in the economy d. An increase in the willingness of people to buy bonds as a hedge against rising prices e. An increase in the willingness of people to buy physical assets as a hedge against rising prices
David Ricardo discovered that two countries can still gain by trading even if one country is more efficient in the production of every commodity. Ricardo's discovery is called the law of
a. comparative advantage. b. absolute advantage. c. compensating balances. d. increasing returns.
A tax elasticity of supply equal to 0.21 indicates that
A. Workers will cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase. B. Employers will hire more workers if tax rates increase. C. Employers will not hire any workers if tax rates increase. D. Workers will not cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.