Determine
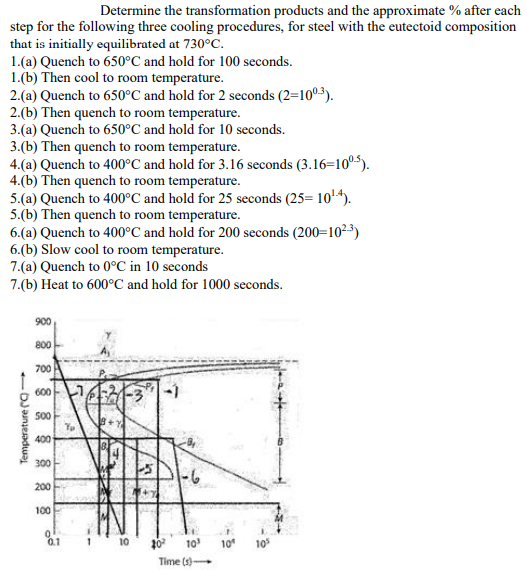
1a. 100% pearlite
1b. 100% pearlite
2a. 100% unstable austenite
2b. 100% martensite
3a. 50% pearlite, 50% unstable austenite
3b. 50% pearlite, 50% martensite
4a. 100% unstable austenite
4b. 100% martensite
5a. 50% bainite, 50% unstable austenite
5b. 50% bainite, 50% martensite
6a. 100% bainite
6b. 100% bainite
7a. 100% martensite
7b. 100% tempered martensite
You might also like to view...
Suppose that two stars are identical in every way; for example, same distance, same mass, same temperature, same chemical composition, and same speed relative to Earth, except that one star rotates faster than the other. Spectroscopically, how could you tell the stars apart?
A) The faster rotating star has wider spectral lines than the slower rotating star. B) The faster rotating star will have an emission line spectrum whereas the slower rotating star will have an absorption line spectrum. C) The peak of thermal emission will be at a shorter wavelength for the faster rotating star than for the slower rotating star. D) There is no way to tell the stars apart spectroscopically because their spectra will be identical.
Where do we observe black holes?
A. In orbit around stars in binary systems. B. In the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C. In the centers of elliptical galaxies. D. In quasars. E. All of the above.
Einstein's theory of relativity is based in part on which one of the following postulates?
a. Mass and energy are equivalent. b. Space and time are absolutes. c. Energy is conserved only in elastic collisions. d. Speed of light in a vacuum is same for all observers regardless of source velocity.
A charged particle is moving with speed v perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. A second identical charged particle is moving with speed 2v perpendicular to the same magnetic field. The frequency of revolution of the first particle is f
The frequency of revolution of the second particle is A) f. B) 4f. C) f/2. D) f/4. E) 2f.