Work is done on an object when you lift it against gravity. How does this work relate to gravitational potential energy? If the lifted object is dropped, what becomes of this energy?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: The work you do on the lifted object may be stored as gravitational potential energy. Then force × distance = weight × height. If the lifted object is dropped, this energy transforms to motion energy—kinetic energy. The kinetic energy it possesses as it returns to its initial position equals the gravitational potential energy at its highest point, which equals the initial work done.
You might also like to view...
A rocket with a mass of 750 grams is launched straight up. It achieves a velocity of 25.00 m/s in 2.00 seconds. The average net force on the rocket is
A. 16.7 N. B. 24.5 N. C. 33.1 N. D. 41.7 N. E. 52.8 N.
A steel hanger with solid cross section has horizontal force P 5 5.5 kN applied at free end D. Dimension variable b 5 175 mm and allowable normal stress is 150 MPa. Neglect self-weight of the hanger. The required diameter of the hanger is approximately:
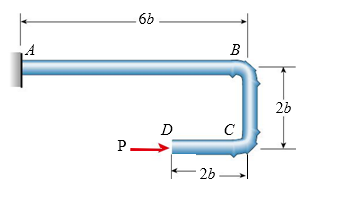
(A) 5 cm
(B) 7 cm
(C) 10 cm
(D) 13 cm
A sealed cylinder fitted with a movable piston contains ideal gas at 27°C, pressure 0.500 × 105 Pa, and volume 1.25 m3. What will be the final temperature if the gas is compressed to 0.800 m3 and the pressure rises to 0.820 × 105 Pa?
A) 42°C B) 68°C C) 130°C D) 250°C E) 150°C
Which of the following numbers is the largest?
A) 23.62 × 108 B) 0.36 × 109 C) 4.35 × 1010 D) 0.056 × 1011