Refer to the information provided in Table 6.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 6.3Dozens of Oysters per DayTotal UtilityMarginal Utility160?2104?3134?4152?5?8Number ofBeers per DayTotal UtilityMarginal Utility140?270?394?4114?5?14Refer to Table 6.3. If the price of a beer is $4, the price of a dozen oysters is $12, and Tyler has $28 of income, Tyler's utility-maximizing combination of beers and oysters per day is
A. 3 beers and 1.5 dozen oysters.
B. 1 beer and 2 dozen oysters.
C. 4 beers and 1 dozen oysters.
D. indeterminate from this information.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Sustained downward movements in the business cycle are referred to as
A) inflation. B) recessions. C) economic recoveries. D) expansions.
Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility:
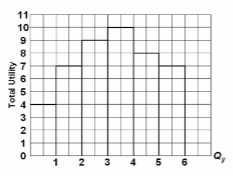
A. increases at an increasing rate.
B. becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output.
C. is found by dividing total utility by the number of units purchased.
D. cannot be calculated from the total utility information.
Explain what happens in the extended aggregate demand and aggregate supply model when there is a recession.
What will be an ideal response?
There are 12 families in a gated community that are affected by air pollution from a local factory. The pollution could be reduced if the company spent $24,000 on upgraded ventilators. The company agrees to install the ventilators if the affected families contribute the $24,000. Since there are no legal restrictions governing the factory's air pollution the negotiations fail. This outcome is an example of the
A. problem that arises when property rights are not defined. B. Coase theorem. C. free-rider problem. D. drop-in-the-bucket problem.