What is the difference between a slowdown in economic growth and a recession?
What will be an ideal response?
A slowdown in economic growth represents an increase in the real output produced in an economy but at a decreasing rate. For example, an economy growing at a steady 3 percent rate may experience a quarter of reduced growth and exhibit an economic growth of 2 percent. Note that the growth of the economy is still positive but lower than in previous quarters. On the other hand, a recession represents negative growth of real output for two consecutive quarters.
You might also like to view...
The collapse of one bank might lead easily to the failure of several others, because ________
A) depositors cannot trust each other to keep their money in the bank B) deposit insurance renders all banks equally fragile C) no bank can survive when its competitors cease to operate D) government regulators will step in to punish any bank suspected of poor management
Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose all the sellers in this market started out charging a price of $45 per unit. What is the most likely result?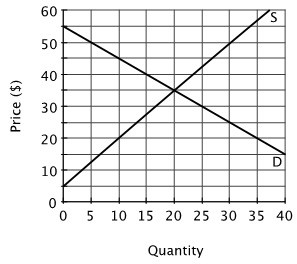
A. They would lower their prices because at $45 there would be excess demand. B. They would all make a large profit because $45 is more than the equilibrium price. C. They would lower their prices because at $45 there would be excess supply. D. They would all just break even because $45 is their reservation price.
As of 2015, per capita GDP in the United States was approximately
A. $37,000. B. $26,000. C. $56,000. D. None of the choices are correct.
For a firm, a decrease in the interest rate resulting from monetary policy can:
A. decrease its net worth. B. decrease the cost of its liabilities. C. decrease the value of its assets. D. all of the answers given are correct.