If the economy is represented in the graph shown and is currently at point E2, what could be said about the state of the economy?
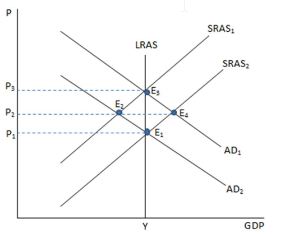
A. There is higher unemployment than the natural rate.
B. There is lower unemployment than the natural rate.
C. The unemployment rate is just about the natural rate.
D. The unemployment rate is zero.
A. There is higher unemployment than the natural rate.
You might also like to view...
The total welfare associated with a market that includes a government sales tax equals
A) consumer surplus plus producer surplus. B) consumer surplus plus producer surplus minus government tax revenue. C) consumer surplus plus producer surplus plus government tax revenue. D) the government tax revenue.
Using the Lorenz curve, the degree of income inequality is measured by
a. The line connecting all points for which a given percentage of families receives exactly the cumulative percentage of income b. the distance of the Lorenz curve from the line of perfect equality c. the flat diagonal line that applies to a perfectly elastic demand curve d. the number of times the Lorenz curve crosses the line of perfect equality e. is derived by dividing the number of people below the poverty line by the total population
Which of the following statements best describes government options during a recession?
a. During a recession, the government will want to implement contractionary fiscal policy, but may be unable to do so because such a policy would lead to a budget deficit. b. During a recession, the government will want to implement discretionary fiscal policy, but may be unable to do so because such a policy would lead to a budget surplus. c. During a recession, the government will want to implement contractionary fiscal policy, but may be unable to do so because such a policy would lead to a budget surplus. d. During a recession, the government will want to implement expansionary fiscal policy, but may be unable to do so because such a policy would lead to a budget deficit.
The marginal cost is the slope of the:
a. marginal product curve. b. total cost curve. c. total product curve. d. long-run average total cost curve.