If the price of a good changes but everything else influencing suppliers' planned sales remains constant, there is a
A) new supply curve that is to the right of the initial supply curve.
B) new supply curve that is to the left of the initial supply curve.
C) movement along the supply curve.
D) rotation of the initial supply curve around the initial price.
C
You might also like to view...
Consumer surplus measures
A) the extra amount that a consumer must pay to obtain a marginal unit of a good or service. B) the excess demand that consumers have when a price ceiling holds prices below their equilibrium. C) the benefit that consumers receive from a good or service beyond what they pay. D) gain or loss to consumers from price fixing.
Weber and Fechner found
A. that the minimally perceptible difference is roughly proportional to the original intensity of the stimulus. B. that it is easier to tell the difference between a 25 and a 50-watt light bulb than it is to tell the difference between a 100-watt bulb and a 300-watt bulb. C. that the minimally perceptible difference is inversely proportional to the original intensity of the stimulus. D. consumers are more likely to drive 10 blocks to save $5 on a $500 television than they are to drive 10 blocks to save $5 on a $25 clock.
Based on the graph showing the effective federal funds rate, the rates in the early 2000s were ______.
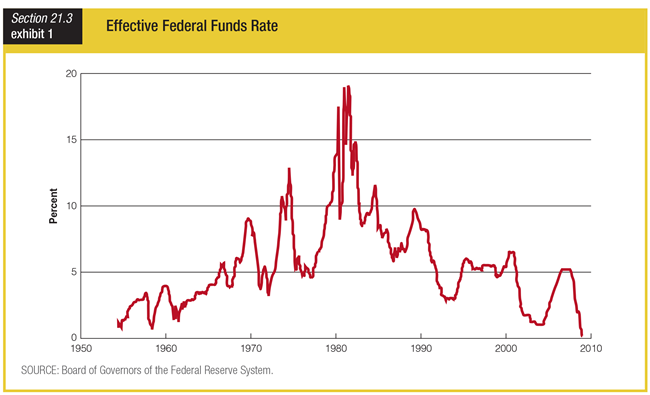
a. the lowest in over 40 years
b. the highest in over 40 years
c. about the average for the past 40 years
d. the only negative rates in over 40 years
If the NAIRU was 4.8% in 2002 and the actual unemployment rate was 5.8%, what percentage of the labor force could have been put to work without exerting upward pressure on inflation?
A. 1% B. 5.3% C. 1.2% D. 10.6%