Five moles of pure W vapor at T=50 ?C and P=0.5 bar is mixed with ten moles of pure Z vapor at T=50 ?C and P=0.5 bar. The resulting mixture is then expanded to a final state of T=50 ?C and P=0.1 bar. What is the total change in entropy of the vapor, in J/K?
This problem concerns mixtures of two compounds, W and Z. At T=50 ?C, the vapor pressures are PWsat = 0.6 bar and PZsat = 1.0 bar. Mixtures of the two compounds at this temperature can be modeled using the one-parameter Margules equation, with A = -1.5.
The mixture can be represented as going through two changes that affect the total change in entropy of the system. Mathematically, this is represented as:
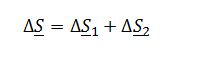
The first change in entropy results from the mixing of the two compounds, and the second is the change in pressure of the gas. Because the system is at low pressures, the first change in entropy can be assumed as that for an ideal solution, while the second change in entropy can be assumed as that for an ideal gas. Replacing the respective terms, the expression above now becomes:
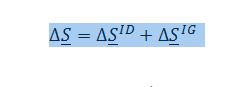
For and ideal solution:
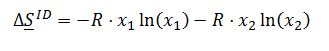
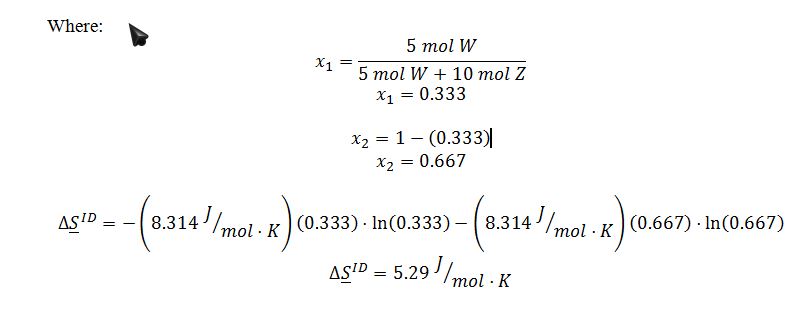
For and ideal gas:
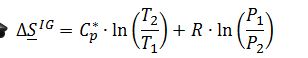
Because there is no change in temperature in this process, the expression simplifies to:
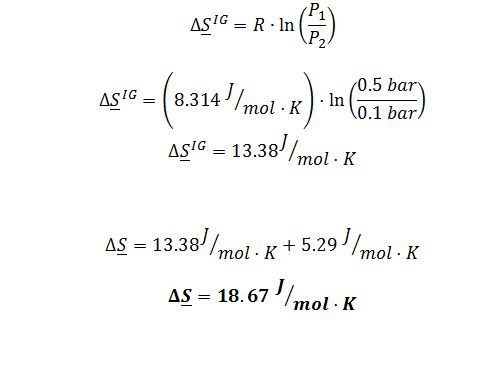
You might also like to view...
What is the maximum ground-level pollutant concentration (mg/m3) from an urban area elevated source with the effective stack height H = 20m, cyanide (HCN) emissions equal to 0.5 g/s, and the average wind velocity = 3 m/s with a stability class C for the atmosphere? Assume ?z = 100 m and ?y = 100m. Note: Assume the source is in an urban area.
What will be an ideal response?
The underlined part of this thread note, 1/2–13UNC–2A, means:
a. threads per inch b. major diameter c. thread series d. class of fit
Transformers are rated by their primary voltage, secondary voltage, and volt-amperes (VA).
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The buildup of water in cells creates an internal pressure called ____________________ that helps the cell retain its shape
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word