There are differences between basic research and applied research. Which of the following would be an applied research question?
a. "What are the basic stages of childhood development?"
b. "How do people respond to a crisis when there are many other people around?"
c. "What are the psychological principals that explain different types of learning?"
d. "Which method is most effective for a person with anxiety to use to stay calm in a stressful situation?"
Answer: d
You might also like to view...
Mental health professionals sometimes use convenience samples of patients who have presented for treatment. Give an example of when this would not be a methodological problem and when it would be a methodological problem
Answer:
Which reason is NOT listed by the textbook as one that makes people especially difficult to study?
A) complexity B) emotionality C) variability D) reactivity
Which of the following statements about attitudes toward homosexuality in America today is most accurate?
A) The majority of Americans believe that same-sex sexual behavior is not wrong. B) Younger Americans are more likely to agree that gay people should be allowed to get married than are older Americans. C) Americans over the last decade have become more negative in their attitudes toward equal rights for homosexual individuals. D) Americans' attitudes toward gay marriage have become more negative since homosexuals have begun to push for legalized gay marriages.
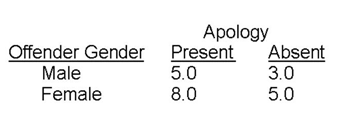
Describe the research design the researcher used, including the type of variables, and identify the conditions that are created using factorial combination.
A researcher examined whether people's responses to injustice depend on whether the offender in a hypothetical scenario is a male or a female, and whether the offender apologized (or not) after the offense. Participants were randomly assigned to the gender of the offender condition (female, male) and apology condition (present, absent).
Participants read a hypothetical scenario in which a person (male or female) acted unjustly and the action results in severe harm. Half of the participants read that the offender apologized; the other half read the same scenario except no apology was mentioned. Participants then rated the extent to which they would forgive the offender using a 0 (no forgiveness) to 9 (complete forgiveness) rating scale. The researcher predicted that participants' forgiveness would be greater following an apology compared to the apology-absent condition. The researcher also predicted that the gender of the offender would have no effect on forgiveness.
The researcher observed the following means: