One mole of an ideal gas is held at a constant pressure of 1 atm. Find the change in volume (in liters) if the temperature changes by 50°C
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
d
You might also like to view...
Calculate the net radiant-heat-transfer rate if the two surfaces in Problem 11.18 are black and are connected by a refractory surface with an area of 500 m2. A1 is at 555 K and A2 is at 278 K. What is the refractory surface temperature?
GIVEN
• Rectangular surfaces A1 and A2 connected by a refractory surface A3
• A1 is parallel to and centered 5 m above A2
• Dimensions of A1 = 1 m × 20 m
• A2 is 20 m2
• A3 is 500 m2
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 555 K
• Temperature of A2 (T2) = 278 K
• A1 and A2 are black
FIND
(a) The net radiating heat transfer rate (q1)
(b) The refractory surface temperature (T3)
SKETCH
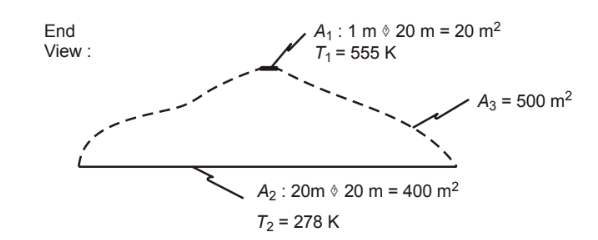
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
Which asteroid did Dawn visit first and which is second in its planned mission?
A) Mathilde, Eros B) Ida, Dactyl C) Vesta, Ceres D) Gaspra, Ida E) Pallas, Ceres
Projectile Motion: An athlete competing in the long jump leaves the ground with a speed of 9.14 m/s at an angle of 35° above the horizontal. How long does the athlete stay in the air, assuming no significant air resistance?
A. 0.50 s B. 0.88 s C. 1.1 s D. 2.5 s E. 0.54 s
Kepler's discovery that T2 /r3 = K applies
A) to orbits where K is a universal constant. B) only to circular orbits. C) to lunar motion provided K is the same for planetary motion. D) to elliptical orbits where r is the average distance.