Calculate the amount to administer per minute: ________. 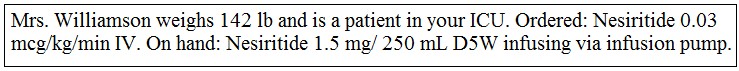
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
0.3 mL/min
Convert mg to mcg
1,000 mcg : 1 mg = x : 1.5 mg
x = 1.5 × 1,000 mcg
x = 1,500 mcg
Concentration of solution is 1,500 mcg/250 mL or 6 mcg/1 mL
Convert weight to kg:
1 kg : 2.2 lb = x : 142 lb
x × 2.2 = 1 kg × 142![]()
x = 64.54, rounded to 64.5 kg
Determine desired dose:
D = 0.03 mcg/kg/min × 64.5 kg
D = 1.935 mcg/min, rounded to 1.9 mcg/min
Determine the amount to administer:
H = 6 mcg; Q = 1 mL; D = 1.9 mcg/min![]()
A = 0.316 mL/min = 0.3 mL/min
You might also like to view...
The patient has just returned to the postsurgical unit after undergoing surgery to remove a lung tumor. During one of the postoperative vital sign checks, the nurse notes that the patient's sys-tolic blood pressure had dropped by 30 points
In addition to the drop in systolic blood pressure, the patient's skin is pale and "clammy." The nurse should do which of the following? a. Report the findings to the health care pro-vider immediately. b. Understand that the patient's arteries are constricting, causing pallor. c. Wait to see if the blood pressure increases in 30 minutes. d. Nothing; this is a normal occurrence fol-lowing a thoracic surgery.
The nurse is caring for four clients on a medical unit. The nurse is most correct to review which client's laboratory reports first for an electrolyte imbalance?
A) A 7-year-old with a fracture tibia B) A 65-year-old with a myocardial infarction C) A 52-year-old with diarrhea D) A 72-year-old with a total knee repair
An adult client has a hematocrit of 64%. The nurse realizes that this laboratory value is most consistent with:
a. dehydration. b. leukemia. c. anemia. d. hemorrhage.
A 6-year-old child is admitted for revision of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt for noncommunicating hydrocephalus. What sign or symptom does the child have that indicates a revision is necessary
a. Tachycardia b. Gastrointestinal upset c. Hypotension d. Alteration in level of consciousness