How do the following affect the equilibrium price in a market?
a. A leftward shift in demand
b. A rightward shift in supply
c. A large rightward shift in demand and a small rightward shift in supply
d. A large leftward shift in supply and a small leftward shift in demand
a. Everything else remaining unchanged, a leftward shift in demand will lower the equilibrium price in the market.
b. Everything else remaining unchanged, a rightward shift in supply will lower the equilibrium price in the market.
c. Both the demand and supply curves will shift to the right but the shift in the demand curve will be greater. This means that that equilibrium price is likely to increase.
d. Both the demand and supply curves will shift to the left but the shift in the supply curve is greater than the shift in the demand curve. This means that the equilibrium price is likely to increase.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following are balance of payments accounts?
i. capital and financial account ii. tariff account iii. current account A) i only B) ii only C) iii only D) i and iii E) ii and iii
In Figure 6-5, if price falls from point A to point B along the unit-elastic demand curve,
A. total expenditure remains unchanged. B. total expenditure increases. C. total expenditure decreases. D. total expenditure first increases and then declines.
During normal times
A) fiscal policy is very effective because it the effects of fiscal policy will swamp automatic stabilizers and time lags can be. B) fiscal policy can immediately correct problems in the economy. C) the Ricardian equivalence theorem makes fiscal policy very effective. D) fiscal policy is not effective because of the recognition time lag.
For a person earning $15,000, the marginal tax amount from 10,001 to $15,000 is:
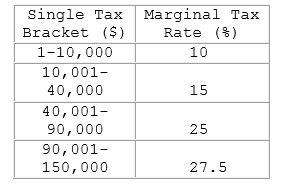
A. $500
B. $750
C. $1,750
D. $2,000