A rural primary road segment of 2 miles long has an average annual daily traffic (AADT) of 11,350. The number of crashes that have occurred over the past 5 years are 5 fatal, 55 injury crashes, and 100 property damage only crashes. Statewide average crashes for this type of roads are 2 fatal, 130 injury, and 300 property damage only crashes per 100 MVMT. The weight factors for fatal, injury, and property damage only crashes are 8, 3, and 1 respectively. Using the critical crash ratio methodology, determine whether this site can be labeled a hazardous site, using a 95 percent confidence limit.
What will be an ideal response?
Step 1. Calculate the traffic base, MEVi, using Equation 5.29

Step 2. Calculate the 3-year average equivalent PDO crash rate for this type of facility.

Step 3. Select a test factor based on confidence level. Since a confidence level of 95% is specified, the test factor is 1.96.
Step 4. Compute the critical rate:
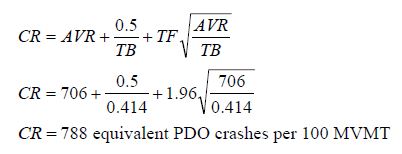
Step 5. Determine the ratio of actual crash occurrence for the segment with respect to the critical rate.
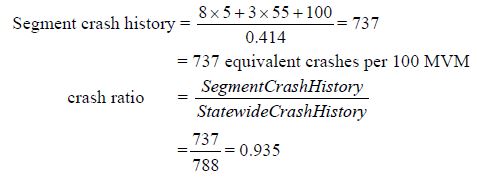
Since the ratio is less than 1, a safety problem is not likely to exist.
You might also like to view...
Proper exhaust manifold tuning actually creates a ____________________, which helps draw exhaust out of the cylinders.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A(n) ____ is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided without losing its identity.
a. atom b. molecule c. element d. compound
State the four Rule #1 requirements.
What will be an ideal response?
Verilog can describe flip-flops but VHDL cannot because VHDL cannot represent a pulse transition detector
Indicate whether the statement is true or false