Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch.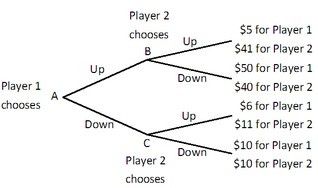 If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
A. Player 2 would commit to choosing Up.
B. Player 2 would commit to mimicking Player 1's strategy.
C. Player 2 would not commit to choosing either strategy.
D. Player 2 would commit to choosing Down.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following groups are typically harmed by unexpected inflation?
a. lenders b. borrowers c. pensioners on fixed incomes d. both (a) and (c).
When someone takes out a loan at a bank, the money supply becomes smaller.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 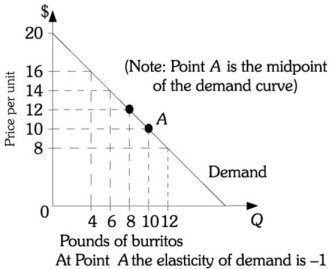 Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3. This firm's total revenue will be maximized at a price of
Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3. This firm's total revenue will be maximized at a price of
A. $12. B. $10. C. $8. D. $6.
In the Keynesian model, suppose the Fed sets a target for the real interest rate. If the IS curve shifts up and to the right, and the Fed wants to keep output unchanged in the short run and the price level unchanged in the long run, what should the Fed do? Use the LR curve to formulate your answer.
What will be an ideal response?