Increases in the productivity of labor tend to
A. increase the marginal revenue product of labor and the wages employers are willing to pay for any given amount of labor.
B. decrease the marginal revenue product of labor and increase the wages employers are willing to pay for any given amount of labor.
C. increase the marginal revenue product of labor but have no effect on the wages employers are willing to pay for any given amount of labor.
D. decrease the marginal revenue product of labor and the wages employers are willing to pay for any given amount of labor.
A. increase the marginal revenue product of labor and the wages employers are willing to pay for any given amount of labor.
You might also like to view...
Suppose an individual has state-independent tastes and invests in risky stocks rather than safe bonds. We can infer that he must be risk loving.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
If Y = $200 billion, c = 0.75, autonomous consumption = $10 billion, and T = $20 billion, induced saving is
A) $25 billion. B) $50 billion. C) $75 billion. D) $150 billion.
Which of the following would be most vulnerable to the tragedy of the commons?
A. Cattle on a ranch B. Restrooms in a restaurant C. Timber on public land D. Apples in Phoebe's apple orchard
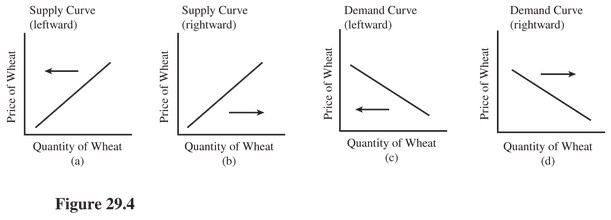 Select the letter of the diagram in Figure 28.1 that best represents the effect of each event on the United States wheat market, ceteris paribus: The European Union tightens restrictions on the agricultural products that can be imported from the United States. (See Figure 29.4.)
Select the letter of the diagram in Figure 28.1 that best represents the effect of each event on the United States wheat market, ceteris paribus: The European Union tightens restrictions on the agricultural products that can be imported from the United States. (See Figure 29.4.)
A. a. B. b. C. c. D. d.