In the long run, a perfectly competitive market will
A) produce only the quantity of output that yields a long-run profit for the typical firm.
B) generate a long-run equilibrium where the typical firm operates at a loss.
C) supply whatever amount consumers demand at a price determined by the minimum point on the typical firm's average total cost curve.
D) supply whatever amount consumers will buy at a price which earns the market an economic profit.
C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.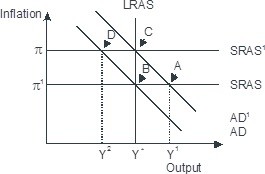
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
The substitution effect of a decrease in the price of movie tickets results in
A) a decrease in the quantity of movie tickets demanded. B) an increase in the demand for movie tickets. C) an increase in the quantity of movie tickets demanded. D) a decrease in the demand for movie tickets.
When a monopolist faces a fixed marginal cost of production, profit is maximized if:
a. the slope of the tangent to the total revenue curve is equal to the slope of the total cost curve. b. the slope of the total cost curve is 1. c. the marginal revenue is zero. d. the slope of the tangent to the total revenue curve is equal to the slope of the marginal revenue curve.
How will an increase in the level of human capital, ceteris paribus, affect an economy's production possibilities curve?
A. Shift the curve inward. B. Result in a movement from inside the curve to a point on the curve. C. Result in a movement along the curve. D. Shift the curve outward.