If the price of a product is above equilibrium, what forces it down?
What will be an ideal response?
When the price is above equilibrium, a surplus occurs. Some producers who are unable to sell the product will have an incentive to offer to sell the product at a lower price. A lower price will simultaneously decrease the quantity supplied and increase the quantity demanded. This downward pressure on price continues until the surplus is eliminated and equilibrium is achieved.
You might also like to view...
Real GDP measures output of final goods and services in physical units
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The TB (i.e., X- M) is part of the short-run spending equation. With sticky prices, what would be the effect on the TB with an increase (depreciation) of the home nation's exchange rate?
a. Consumers in the home nation would find it more expensive to buy domestic goods compared to foreign goods, and the trade balance would decrease. b. Consumers in the home nation would cut back on both domestic and foreign goods and the trade balance would decrease. c. Consumers in the home nation would increase spending on both domestic and foreign goods, and the trade balance would be unchanged. d. Consumers in the home nation would increase spending on domestic goods and decrease spending on foreign goods, causing the trade balance to increase.
Which of the following is NOT a method for promoting global economic growth?
A. Count on developed nations to develop policies that promote economic growth in developing nations. B. Rely on private markets to direct capital goods toward their best use. C. Encourage population growth so that developing nations' labor supply increases. D. market based approach
Refer to the table. An increase in net exports of $10 would:
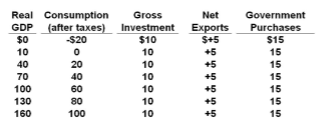
A. increase real GDP by $10.
B. increase real GDP by $30.
C. decrease real GDP by $10.
D. decrease real GDP by $30.