Welfare programs satisfy the criteria of the benefit principle
a. True b. False
b
You might also like to view...
The quantity demanded of a good or service is the quantity that a consumer
A) is willing to buy at a particular price during a given time period. B) actually buys at a particular price during a given time period. C) needs to buy at a particular price during a given time period. D) should buy at a particular price during a given time period.
What does price elasticity of demand measure? When is demand elastic? Inelastic? Unit elastic?
What will be an ideal response?
Consider the following simple regression model: y = 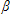
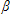
src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Ch_15_Instrumental_Variables_Estimation_and_Two_Strage_Least_Squares__media__d15d8088-6a26-4e76-8757-cf8a8c5ae58c.PNG" style="vertical-align:middle;" />0and 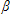
0 and Cov (z,u) = 0. The variable z is called a(n) _____ variable.
A. dummy
B. instrumental
C. lagged dependent
D. random
In what way does long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition differ from long-run equilibrium under perfect competition?
A) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive and allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve neither allocative nor productive efficiency. B) The only difference is that in a monopolistically competitive market there are many brands to choose from while in a perfectly competitive market there is one standard product. C) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve allocative efficiency. D) Firms in perfect competition achieve allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve brand efficiency.