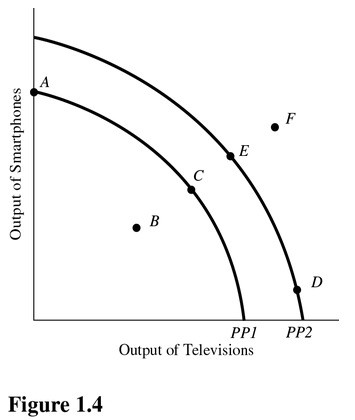
 In Figure 1.4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
In Figure 1.4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2 could be caused by
A. Tougher pollution controls for the producers of televisions and smartphones.
B. Implementation of training programs that improve the skills of workers.
C. An increase in the unemployment rate.
D. A flu epidemic that makes many workers sick.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
In the multiple-polluter case for a pollution permit system, suppose Firm 1 and Firm 2 face marginal abatement cost functions of MAC1 = 4.5A1 and MAC2 = 2.25A2, respectively. If the government issues each firm tradeable pollution permits such that each has to abate 10 units of pollution, then, based on this allocation,
a. the two firms have no incentive to trade b. firm 1 has an incentive to buy a permit if the price is greater than $45 c. firm 2 has an incentive to buy a permit if the price is above $22.50 d. firm 2 will be willing to sell a permit if the price is above $22.50
The fact that there is a very limited amount of land in Hong Kong means the supply of new apartments in Hong Kong is
A) inelastic. B) elastic. C) unit elastic. D) perfectly elastic. E) limited by the demand.
Suppose the money wage rate and the price level both fall by 5 percent. As a result
A) the quantity of labor demanded increases. B) the quantity of labor demanded decreases. C) the quantity of labor demanded does not change because there is no change in the real wage. D) people are worse off and there is more unemployment.
Suppose in a democratic society, all voters prefer choice G over choice B; however, when the two choices are presented along with a third choice, R, B wins the election. This violates the assumption of
A) transitivity. B) non-dictatorship. C) independence of irrelevant alternatives. D) completeness.