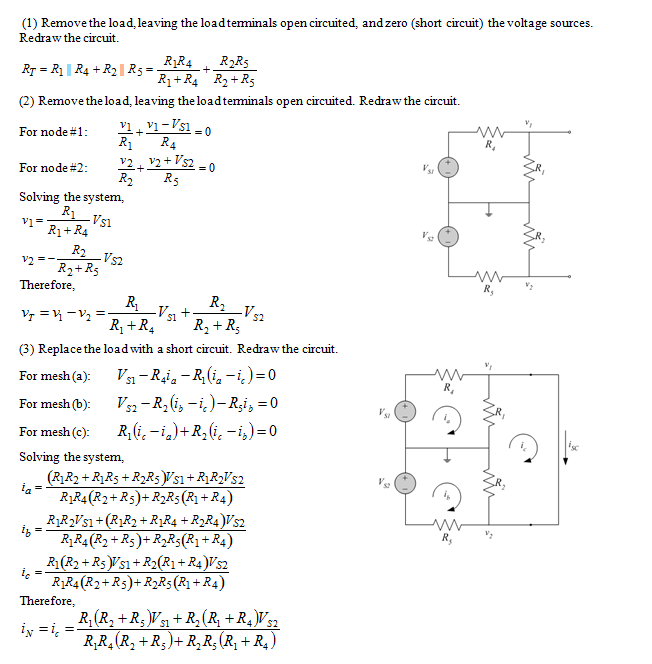
Find the Thévenin equivalent resistance seen by resistor R3 in the circuit of Figure P3.5. Compute the Thévenin (open-circuit) voltage and the Norton (short-circuit) current, from node A to node B, when R3 is the load.
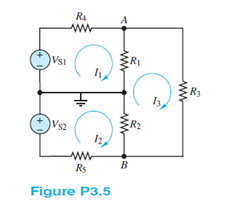
Find:
The Thévenin equivalent resistance seen by resistor R3, the Thévenin (open-circuit) voltage and the Norton (short-circuit) current when R3 is the load.
Analysis:
You might also like to view...
A drawer contains 6 red socks, 4 green socks, and 2 black socks. Two socks are chosen at random. What is the probability that they match?
What will be an ideal response?
Match the type of solderless wire terminal to its best application. Note: The choices may be used more than once.
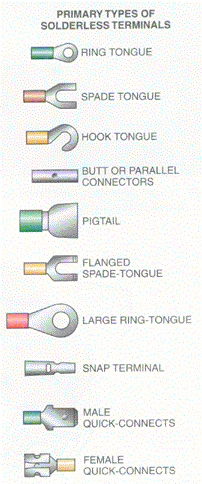
A. Used to connect a wire under a screw terminal when screw has been completely removed B. Used to connect a wire under a screw without completely removing screw C. D. Used to join two pieces of wire together E. F. G. Used to connect a wire to a "male terminal"
When using a floor jack, you should not work under a vehicle until it is fully raised and well balanced on the jack with the handle in an upright position.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits at terminals a-b of the circuit in Fig. 10.110.
 FIGURE 1.png)