Comparative advantage is the ability, compared with another producer
A) to produce more of a product with the same resources.
B) to use fewer inputs to produce the same amount of a product.
C) to produce a higher-quality product with fewer resources.
D) to produce an additional unit of a product at lower opportunity cost.
D
You might also like to view...
Excess reserves that are voluntarily held by institutions are called:
a. Customary reserves. b. Bank equity. c. Normal reserves. d. Funny money. e. Federal funds.
When dealing with present value, a higher interest rate:
A. does not affect the present value of the future amount. B. decreases the present value of a future amount. C. increases the present value of a future amount. D. None of the statements associated with this question are correct.
In terms of the decisions coming from the Euro system's Governing Council, explain why, at times, relatively small countries may be at a distinct disadvantage in terms of monetary policy targets but perhaps have undue influence in terms of the actual policies.
What will be an ideal response?
Assume the price of a product sold by a purely competitive firm is $5. Given the data in the accompanying table, at what output level is total profit highest in the short run?
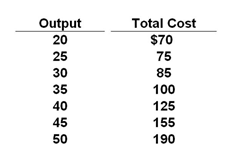
A. 20
B. 30
C. 40
D. 50