Let X ~ Geom(p). Let s ? 0 be an integer.
a. Show that P(X > s) = (1 ?p)s.
b. Let t ?0 be an integer. Show that P(X > s + t|X > s) = P(X > t). This is the memoryless property.
c. A penny and a nickel are both fair coins. The penny is tossed three times and comes up tails each time. Now both coins will be tossed twice each, so that the penny will be tossed a total of five times and the nickel will be tossed twice. Use the memoryless property to compute the conditional probability that all five tosses of the penny will be tails, given that the first three tosses were tails. Then compute the probability that both tosses of the nickel will be tails. Are both probabilities the same?
You might also like to view...
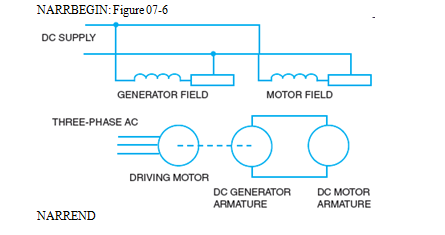
Refer to the accompanying figure. Basic electrical theory of a DC motor-generator, variable speed control system. Briefly explain how speeds above the motor base speed (nameplate speed) and speeds below the motor base speed are obtained.
What will be an ideal response?
Create a law that would be beneficial to the animal being confined with
minimal impact on the producer. What would be the drawbacks of your law?
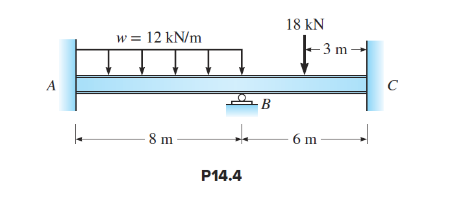
What will be an ideal response?Analyze the beam in Figure P14.4. After member end moments are determined, compute all reactions and draw the moment diagrams. EI is constant.
What would happen if the narrow spray angle nozzle were used in a round combustion chamber?
What will be an ideal response?