The average density of the planet Jupiter has been known for hundreds of years, but the densities of its Galilean moons were only determined accurately from data obtained during the Voyager by-pass missions. Why?
What will be an ideal response?
The density of an object is its mass divided by its volume. Although the sizes of the Galilean moons have been known approximately for some time, their masses have not. The Voyager missions helped determine these masses and, therefore, their densities.
You might also like to view...
Multiple-Object Accelerating Systems: A locomotive is pulling three train cars along a level track with a force of 100,000 N. The car next to the locomotive has a mass of 80,000 kg, the next one, 50,000 kg, and the last one, 70,000 kg. You can neglect the friction on the cars being pulled.(a) What is the magnitude of the force between that the 80,000-kg car exerts on the 50,000-kg car?(b) What is the magnitude of the force that the 50,000-kg car exerts on the 70,000-kg car?
What will be an ideal response?
At which lunar phase(s) are tides most pronounced (for example, the highest high tides)?
A) both new and full moons B) both first and third quarters C) full moon only D) new moon only E) third-quarter moon only
A rod is 2.40 m long and has a diameter of 2.50 mm. A force of 2000 N is applied to the end to stretch the rod by 1.00 mm. What is the tensile modulus for this rod?
a. 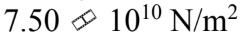
b. 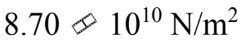
c. 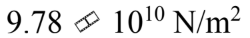
d. 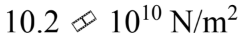
e. 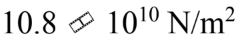
J. Robert Oppenheimer was
A) the head of the program to develop the world's first fusion bomb. B) the inventor of radiation therapy. C) the head of the program to develop the world's first fission bomb. D) the discoverer of nuclear fission. E) the head of the program to develop the world's first nuclear reactor.