Regarding the stock market crash of 1929, evidence shows that
(a) no one expected trouble in the stock market before the October 1929 crash.
(b) there was doubt about the speculative heights of stock prices as they continued to
rise and more money continued to pour into the market.
(c) only active support by the New York Federal Reserve Bank during the summer and
fall of 1929 enabled the bull market to last until October.
(d) investment trusts and nonbanking money sources correctly anticipated the downturn.
(b)
You might also like to view...
What is the real exchange rate between the dollar and the euro equal to?
What will be an ideal response?
By 2010, the U.S. economy had emerged from the recession that had begun in 2007. Despite an economic growth rate well above zero, unemployment showed little sign of declining much below ten percent
Focusing on the definition of the unemployment rate, explain how it is possible to have positive economic growth without declining unemployment.
A firm is currently operating where the MC of the last unit produced = $64, and the MR of this unit = $70 . What would you advise this firm to do?
a. Shut down. b. Increase output. c. Stay at current output. d. Decrease output. e. Decrease price.
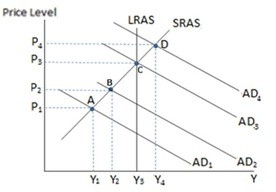 Assuming the economy in the graph shown is currently at equilibrium A, if the government wanted to enact a policy it would likely enact:
Assuming the economy in the graph shown is currently at equilibrium A, if the government wanted to enact a policy it would likely enact:
A. contractionary fiscal policy in an effort to move aggregate demand to the left. B. contractionary fiscal policy in an effort to move aggregate demand to the right. C. expansionary fiscal policy in an effort to move aggregate demand to the right. D. expansionary fiscal policy in an effort to move aggregate demand to the left.