Geographical conditions such as good climate, availability of natural resources, and fertile soil are examples of:
A) proximate causes of prosperity. B) implicit causes of prosperity.
C) fundamental causes of prosperity. D) explicit causes of prosperity.
C
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 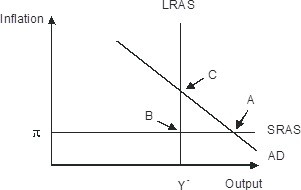
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
If the money wage rate is constant and the price level increases, what happens to the real wage rate, firms' profits, and the aggregate quantity supplied?
What will be an ideal response?
Karlos sells his product for $40 each in a competitive price-taker market. At his present rate of output, his marginal cost is $39, average variable cost is $25, and average total cost is $45 . To improve his profit/loss situation, Karlos should
a. increase output b. reduce output but not to zero c. maintain the present rate of output d. shut down e. raise the price
if the per capita income of a country is growing at 3.5 percent per year, approximately how long will it take for that income to double?
What will be an ideal response?