Perform the indicated operations given the matrices.Let A = 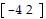 and B =
and B = 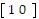 ; 2A + 3B
; 2A + 3B
A. 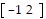
B. 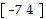
C. 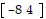
D. 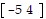
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Find all the second order partial derivatives of the given function.f(x, y) = cos xy2
A. fxx(x, y) = y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2[2y2 cos (xy2) - sin (xy2)] ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2y[y2 cos (xy2) - sin (xy2)]
B. fxx(x, y) = -y4 cos xy2; fyy(x, y) = - 2x[2xy2 cos (xy2) + sin (xy2)]; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = - 2y[xy2 cos (xy2) + sin (xy2)];
C. fxx(x, y) = - y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2[ sin (xy2)- 2y2 cos (xy2)] ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2y [sin (xy2)-y2 cos (xy2)]
D. fxx(x, y) = - y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2y ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2
; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2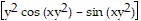
Perform the indicated operation and simplify. Write the answer in the form a + bi.
A.  i
i
B. -  i
i
C. - 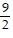 i
i
D. 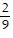 i
i
Find a cubic polynomial in standard form with real coefficients having the given zeros.1 and 2 - 3i
What will be an ideal response?
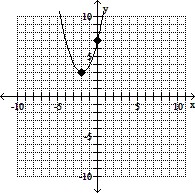
Graph the quadratic equation. Determine the x-intercepts, if they exist. Identify the vertex and axis of symmetry.y = x2 + 4x - 7
A. vertex: (- 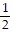 , -
, -  )
)
x-intercepts: (-4, 0) and (3, 0)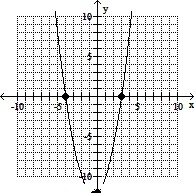
B. vertex: (4, 0)
x-intercept: (4, 0)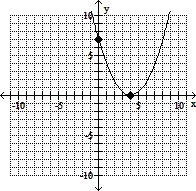
C. vertex: (-2, -11)
x-intercepts: (-2 ± 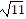 , 0)
, 0)
D. vertex: (-2, 3)
x-intercepts: none