How do we measure economic growth?
a. Increases in the price level, as indicated by the GDP chain price index.
b. Increases in nominal GDP.
c. Increases in real GDP.
d. Increases in the labor force.
c
You might also like to view...
If central banks were no longer obliged to intervene in currency markets to fix exchange rates, governments would be able to use monetary policy to reach
A) internal balance. B) external balance. C) internal and external balance. D) internal but not external balance. E) external but not internal balance.
Suppose Brandon's indifference curves are defined as U = (3/4)?FS + (1/4)?FH, where FS is consumption during sunny weather and FH is consumption during a hurricane. Further suppose Brandon receives 64 units of food when it is sunny and 16 units when there is a hurricane. What is the certainty equivalent of the expected food consumption bundle if the probability of sunshine is ? = 0.75?
A. 49 units of food B. 52 units of food C. 7 units of food D. 25 units of food
If the economy in the graph shown is at point D, and the government wished to bring the economy back to its long-run equilibrium, it might:
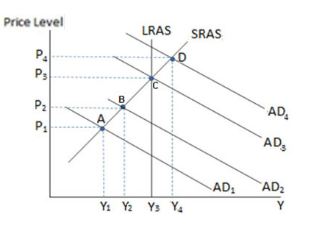
A. increase government spending.
B. decrease income taxes.
C. increase corporate income taxes.
D. All of these would bring the economy back to potential GDP.
The CPI differs from the GDP deflator in that
a. the CPI is a price index, while the GDP deflator is an inflation index. b. substitution bias is not a problem with the CPI, but it is a problem with the GDP deflator. c. increases in the prices of foreign produced goods that are sold to U.S. consumers show up in the CPI but not in the GDP deflator. d. increases in the prices of domestically produced goods that are sold to the U.S. government show up in the CPI but not in the GDP deflator.