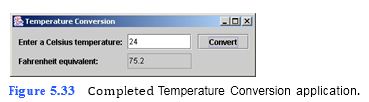
(Temperature Conversion Application) Write an application that converts a Celsius temperature, C, to its equivalent Fahrenheit temperature, F. Figure 5.33 displays the com- pleted application. Use the following formula:
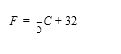
a) Copying the template to your working directory. Copy the C:Examples Tutorial05ExercisesTemperatureConversion directory to your C:Simply- Java directory.
b) Opening the template file. Open the TemperatureConversion.java file in your text editor.
c) Clearing the result when a new value is input by the user. Scroll to the event handler celsiusJTextFieldKeyPressed (lines 99–102). In the body of the event handler, insert a statement that clears the Fahrenheit equivalent: JTextField (named fahr- enheitJTextField) whenever the user enters new input.
d) Coding the convertJButtonActionPerformed event handler. Locate the event han- dler convertJButtonActionPerformed (immediately after the event handler cel- siusJTextFieldKeyPressed). In its body, insert a statement that gets the number in the celsiusJTextField, converts
```
1 // TemperatureConversion.java
2 // Application that converts a Celsius temperature to its equivalent
3 // Fahrenheit temperature.
4 import java.awt.*;
5 import java.awt.event.*;
6 import javax.swing.*;
7
8 public class TemperatureConversion extends JFrame
9 {
10 // JLabel and JTextField for Celsius input
11 private JLabel celsiusJLabel;
12 private JTextField celsiusJTextField;
13
14 // JLabel and JTextField for Fahrenheit output
15 private JLabel fahrenheitJLabel;
16 private JTextField fahrenheitJTextField;
17
18 // JButton to initiate Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion
19 private JButton convertJButton;
20
21 // no-argument constructor
22 public TemperatureConversion()
23 {
24 createUserInterface();
25 }
26
27 // create and position GUI componments; register event handlers
28 private void createUserInterface()
29 {
30 // get content pane for attaching GUI components
31 Container contentPane = getContentPane();
32
33 // enable explicit positioning of GUI components
34 contentPane.setLayout( null );
35
36 // set up celsiusJLabel
37 celsiusJLabel = new JLabel();
38 celsiusJLabel.setText( "Enter a Celsius temperature:" );
39 celsiusJLabel.setBounds( 10, 10, 170, 24 );
40 contentPane.add( celsiusJLabel );
41
42 // set up celsiusJTextField
43 celsiusJTextField = new JTextField();
44 celsiusJTextField.setBounds( 180, 10, 100, 24 );
45 contentPane.add( celsiusJTextField );
46 celsiusJTextField.addKeyListener(
47
48 new KeyAdapter() // anonymous inner class
49 {
50 // called when key pressed in celsiusJTextField
51 public void keyPressed( KeyEvent event )
52 {
53 celsiusJTextFieldKeyPressed( event );
54 }
55
56 } // end anonymous inner class
57
58 ); // end call to addKeyListener
59
60 // set up fahrenheitJLabel
61 fahrenheitJLabel = new JLabel();
62 fahrenheitJLabel.setText( "Fahrenheit equivalent:" );
63 fahrenheitJLabel.setBounds( 10, 40, 170, 24 );
64 contentPane.add( fahrenheitJLabel );
65
66 // set up fahrenheitJTextField
67 fahrenheitJTextField = new JTextField();
68 fahrenheitJTextField.setEditable( false );
69 fahrenheitJTextField.setBounds( 180, 40, 100, 24 );
70 contentPane.add( fahrenheitJTextField );
71
72 // set up convertJButton
73 convertJButton = new JButton ();
74 convertJButton.setText( "Convert" );
75 convertJButton.setBounds( 290, 10, 80, 24 );
76 contentPane.add( convertJButton );
77 convertJButton.addActionListener(
78
79 new ActionListener() // anonymous inner class
80 {
81 // method called when convertJButton is pressed
82 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
83 {
84 convertJButtonActionPerformed( event );
85 }
86
87 } // end anonymous inner class
88
89 ); // end call to addActionListener
90
91 // set properties of application’s window
92 setTitle( "Temperature Conversion" ); // set title bar text
93 setSize( 385, 100 ); // set window size
94 setVisible( true ); // display window
95
96 } // end method createUserInterface
97
98 // clear fahrenheitJTextField because the value is now invalid
99 private void celsiusJTextFieldKeyPressed( KeyEvent event )
100 {
101 // clear fahrenheitJTextField
102 fahrenheitJTextField.setText( "" );
103
104 } // end method celsiusJTextFieldKeyTyped
105
106 // convert Celsius value to Fahrenheit value
107 private void convertJButtonActionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
108 {
109 // get Celsius value input by user
110 int celsius = Integer.parseInt( celsiusJTextField.getText() );
111
112 // calculate equivalent Fahrenheit temperature
113 double fahrenheit = 9.0 / 5.0 * celsius + 32;
114
115 // display Fahrenheit equivalent
116 fahrenheitJTextField.setText( String.valueOf( fahrenheit ) );
117
118 } // end method convertJButtonActionPerformed
119
120 // main method
121 public static void main( String args[] )
122 {
123 TemperatureConversion application =
124 new TemperatureConversion();
125 application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
126
127 } // end method main
128
129 } // end class TemperatureConversion
```
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true concerning the Clipboard object?
(A) It is used to produce the Microsoft Help. (B) It is used to create a text file that permanently maintains copied items on the hard drive. (C) It is an object that appears on the form and is raised by its Click event. (D) It is a portion of memory that holds information and has no properties or events.
Answer the following questions true (T) or false (F)
1. Procedural abstraction involves information hiding in that only the 'contract' between the programmer using the function (the client) and author of a function is known to either. 2. A sequence of calls to the library function rand() generates mathematically correct random number sequences.
More unintentional errors occur in applications when the variables are declared using the minimum scope needed.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
State whether each of the following is true or false. If false, explain why.
1) Structures may contain only one data type. 2) Members of different structures must have unique names. 3) Keyword typedef is used to define new data types. 4) Structures are always passed to functions by reference.