5. When does equilibrium occur?
a. when quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
b. when demand equals supply
c. when consumers buy as much of the good as they want
d. when suppliers sell as much of the good as they want
a. when quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) Chess is an example of a sequential game. 2) A terminal node in a game tree is the starting point of the game. 3) In an entry game, it is not necessary for managers to consider the best response of their competitor(s). 4) If Happy Feet advertises that it will undercut any competitor's price to keep another firm from entering the market, advertising will both increase and decrease Happy Feet's profit. 5) All else equal, the greater the cost of a commitment to prevent a rival firm from entering the market, the less likely the commitment will be undertaken.
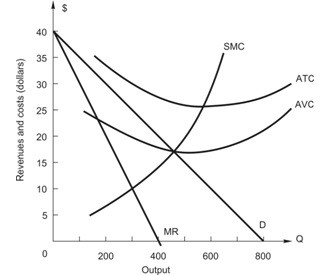 The figure above shows the demand and cost curves facing a price-setting firm. In profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) equilibrium, the price-setting firm earns ________ in total revenue, which is ________ the maximum possible total revenue of ________.
The figure above shows the demand and cost curves facing a price-setting firm. In profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) equilibrium, the price-setting firm earns ________ in total revenue, which is ________ the maximum possible total revenue of ________.
A. $8,000; equal to; $8,000 B. $8,000; more than; $7,500 C. $7,650; less than; $8,000 D. $7,500; less than; $8,000 E. $7,500; equal to; $7,500
Summarize how the law of supply explains the effects of price on the quantity supplied
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the information provided in Table 13.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 13.3Price ($)Quantity4.001003.502003.003002.504002.005001.506001.00700Refer to Table 13.3. If a monopoly faces the demand schedule given in the table and has a constant marginal and average cost of $1 per unit of providing the product, what price should it charge per unit of output so as to maximize its profits?
A. $2.00 B. $2.50 C. $3.00 D. $3.50