Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose the solid line shows the current demand for coffee. In response to news that next year's coffee harvest will be extremely good due to favorable weather conditions, you should expect: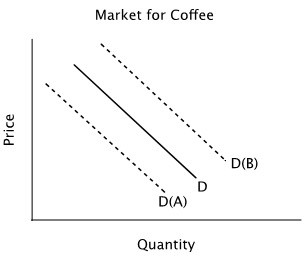
A. the quantity of coffee demanded to decrease, but no shift in the demand curve.
B. the demand curve to shift to D(B) in anticipation of lower future prices.
C. the demand curve to shift to D(A) in anticipation of lower future prices.
D. neither a change in quantity demanded nor a shift in demand because it will be a long time before next year's coffee crop is harvested.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The price of pizza falls by 25 percent. If the elasticity of demand for pizza is equal to –1.5, what will happen to the quantity of pizza demanded?
What will be an ideal response?
The guiding function of price is
A) the movement of price to clear the market of any shortages or surpluses. B) the use of price as a signal to guide government on the use of market subsidies. C) a long-run function resulting in the movement of resources into or out of markets. D) the movement of price as a result of changes in the demand for a product.
The types of problems in principal-agent relationships typically include
a. adverse selection - whom to hire b. moral hazard - how to motivate workers c. uncertainty - how many workers will be needed d. Both A&B
Suppose Debbie is willing to pay $50 for a pair of shoes but has to pay $20 because the shoes are on sale. Her consumer surplus is:
a. ?$20. b. ?$50. c. ?$70. d. ?$30. e. ?$25.