An individual has preferences consistent with standard expected utility theory. They have utility function U(x) over wealth x. Starting with initial wealth of $10,000, the person is then faced with two choice problems. The first involves a choice between (A) no gamble and (B) a gamble with an equal chance of winning $1,800 and losing $1,000 . The second choice problem, the person first has $1,000
taken away (resulting in the adjustment of the reference point). The choice is then between (C) being given back $1,000 for sure and (D) an equal chance of winning $2,800 or nothing. What can be said about the choices the person would make?
a. The person would never choose both A and D.
b. The person would never choose both A and C.
c. The person would choose A and D.
d. The person would choose A and C.
a
You might also like to view...
If an epidemic hits a Malthusian economy, the long-term consequence is
A) an increase in the standard of living. B) a reduction in the standard of living. C) no change in the standard of living. D) dependent on the population growth rate.
Economic growth is represented by a: a. leftward shift of a production possibilities curve
b. rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS). c. horizontal long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS). d. downward shift of an aggregate production function.
When a U.S. citizen buys $500 of Chinese-made parts for a motorcycle,
a. U.S. consumption falls by $500, U.S. net exports decline by $500, and U.S. GDP declines by $1000. b. U.S. consumption does not change, U.S. net exports decline by $500, and U.S. GDP declines by $500. c. U.S. consumption increases by $500, U.S. net exports remain the same, and U.S. GDP increases by $500. d. U.S. consumption increases by $500, U.S. net exports decline by $500, and U.S. GDP remains the same.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 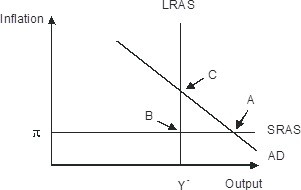
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward