Given K equally sized clusters, the probability that a randomly chosen initial centroid will come from any given cluster is 1/K, but the probability that each cluster will have exactly one initial centroid is much lower. (It should be clear that having one initial centroid in each cluster is a good starting situation for K-means.) In general, if there are K clusters and each cluster has n points, then the probability, p, of selecting in a sample of size K one initial centroid from each cluster is given by Equation 8.1. (This assumes sampling with replacement.) From this formula we can calculate, for example, that the chance of having one initial centroid from each of four clusters is 4!/44 = 0.0938.
![]()
(a) Plot the probability of obtaining one point from each cluster in a sample
of size K for values of K between 2 and 100.
For K clusters, K = 10, 100, and 1000, find the probability that a
sample of size 2K contains at least one point from each cluster. You can
use either mathematical methods or statistical simulation to determine
the answer.
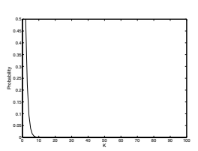
(a) The solution is shown in Figure 4. Note that the probability is essen-
tially 0 by the time K = 10.
(b) We used simulation to compute the answer. Respectively, the proba-
bilities are 0.21, < 10?6, and < 10?6.
Proceeding analytically, the probability that a point doesn’t come from
a particular cluster is, 1 ? 1
K , and thus, the probability that all 2K
points don’t come from a particular cluster is (1 ? 1
K )2K. Hence, the
probability that at least one of the 200 points comes from a particular
cluster is 1 ? (1 ? 1
K )2K. If we assume independence (which is too
optimistic, but becomes approximately true for larger values of K), then
an upper bound for the probability that all clusters are represented in
the final sample is given by (1?(1? 1
K )2K)K. The values given by this
bound are 0.27, 5.7e-07, and 8.2e-64, respectively.
You might also like to view...
The amount charged to borrow money or the amount earned in a savings account is called the ________
A) interest rate B) future value C) rate of return D) present value
A named sequence of statements that performs a task is called a(n):
A) ActiveX. B) function. C) procedure. D) module.
When you attach & after the dataType in the formal parameter list of a function, the variable following that dataType becomes a(n) ____________________ parameter.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
When using DNS for load balancing to support multiple Web servers, each Web server gets its own (usually) public ____________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).