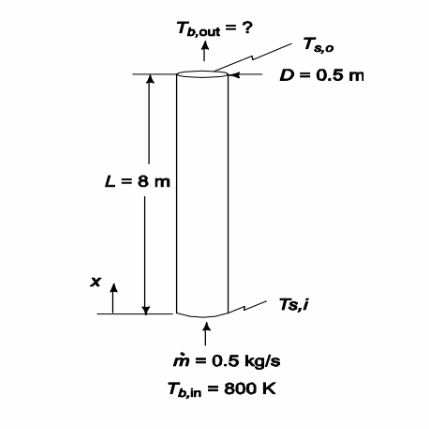
Exhaust gases having properties similar to dry air enter a thin-walled cylindrical exhaust stack at 800 K. The stack is made of steel and is 8-m-tall and 0.5 m inside diameter. If the gas flow rate is 0.5 kg/s and the heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface is 16 W/(m2 K), estimate the outlet temperature of the exhaust gas if the ambient temperature is 280 K.
GIVEN
• Gas properties are similar to dry air
• Gas entrance temperature (Tb,in) = 800 K
• Length of stack (L) = 8 m
• Diameter of stack (D) = 0.5 m
• Mass flow rate (m
) = 0.5 kg/s
• Heat transfer coefficient on the outer surface ( h ,c o ) = 16 W/(m2 K)
• Ambient temperature (T?) 280 K FIND
• The outlet temperature of the exhaust gas (Tb,out)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Radiation heat transfer is negligible
• Natural convection can be neglected
• The inlet to the stack is sharp-edged
• Thermal resistance of the stack wall is negligible
SKETCH
For this problem, neither the heat flux nor the surface temperature will be constant. However, the ambient temperature will be constant, therefore, can be applied by replacing the surface temperature (Ts) with the constant ambient temperature (T?) and replacing hc with U where
U = Overall heat transfer coefficient = 1

This results in the following version
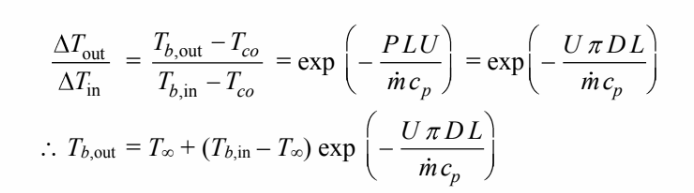
The internal heat transfer coefficient and the average fluid properties will depend on the outlet bulk fluid temperature, therefore, an iterative procedure is required. For the first iteration, let Tb,out = 500 K.
From for dry air at the average bulk temperature of 650 K
Specific Heat (cp) = 1056 J/(kg K)
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0472 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?) = 31.965 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The Reynolds number for flow in the stack is
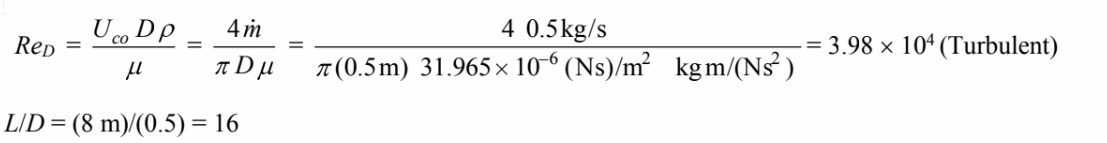
L/D = (8 m)/(0.5) = 16
Since 2 < L/D < 20, the flow will not be fully developed, therefore, the correlation of Molki and
Sparrow for sharp-edged inlets, will be used to correct the correlation of Dittus-Boelter,
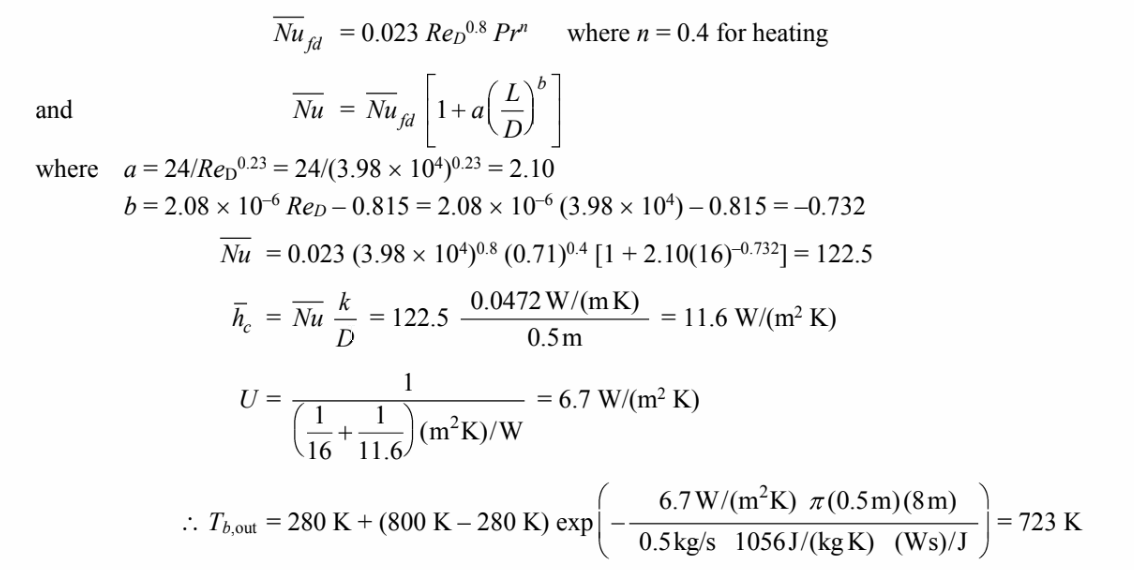
Another iteration using the same procedure yields
Average bulk temperature = 762 K
Specific Heat (cp) = 1074 J/(kg K)
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0534 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?) = 35.460 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.72
Reynolds number (ReD) = 3.59 × 104
Heat transfer coefficient ( ci h ) = 12.1 W/(m2 K)
Outlet temperature (Tb,out) = 722 K
The outlet gas temperature = 722 K
You might also like to view...
Which previously unknown planet's location was predicted from mathematical calculations of orbital motions?
A) Mercury B) Uranus C) Neptune D) Pluto E) all of the above
When radium-223 (Z = 88) decays to radon-119 (Z = 86), the other particle emitted is a(n) __________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
During an isothermal process, 5.0 J of thermal energy via the process of heating is removed from an ideal gas. What is the change in internal (thermal) energy of the gas?
A) 0 J B) 2.5 J C) 5.0 J D) 10 J
A solenoid 4.0 cm in radius and 4.0 m in length has 8000 uniformly spaced turns and carries a current of 5.0 A. Consider a plane circular surface (radius = 2.0 cm) located at the center of the solenoid with its axis coincident with the axis of the solenoid. What is the magnetic flux through this surface? (1 Wb = 1 T ? m2)
A. 63 ?Wb B. 16 ?Wb C. 0.25 mWb D. 10 ?Wb E. 5.0 ?Wb