An object is in front of a concave spherical mirror, and its image is 4.0 cm behind the mirror. If the focal length of the mirror has a magnitude of 5.0 cm, where is the object?
A) 2.2 cm in front of the mirror
B) 2.2 cm behind the mirror
C) 9.0 cm in front of the mirror
D) 1.0 cm behind the mirror
A
You might also like to view...
A pitcher claims he can throw a baseball with as much momentum as a 3.00-g bullet moving with a speed of 1500 m/s. A baseball has a mass of 0.145 kg. What must be its speed if the pitcher's claim is valid?
What will be an ideal response?
If the total energy of an electron in an accelerator is three times its rest energy, what is its speed? (c = 3.00 × 10^8 m/s)
a. 2.00 × 10^8 m/s b. 1.30 × 10^8 m/s c. 1.41 × 10^8 m/s d. 2.98 × 10^8 m/s e. 2.83 × 10^8 m/s
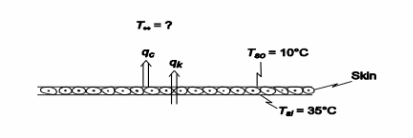
Using the information estimate the ambient air temperature that could cause frostbite on a calm day on the ski slopes.
GIVEN
• Skier’s skin of thickness (L) = 3 mm = 0.003 m exposed to cold air
• Inner surface temperature of skin (Tsi) = 35°C
• Thermal conductivity of skin (k) = 0.35 W/(m K)
• Convective heat transfer coefficient in still air ( ch ) = 20 W/(m2 K)
• Frostbite occurs at an outer skin surface temperature (Tso) = 10°C FIND
• The ambient air temperature (T?) that could cause frostbite ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state conditions prevail
• One dimensional conduction occurs through the skin
• Radiative loss (or gain from sunshine) is negligible
SKETCH
The range of distances that has remained habitable for the entire duration of the Sun's lifetime is referred to as the
A) continuously habitable zone B) habitable zone of consistency C) zone of water stability D) permanently habitable zone