Critics of trade adjustment assistance argue that:
A. the small fraction of workers losing jobs to international trade are no more deserving of assistance than others suffering job loss.
B. it raises prices for consumers.
C. it keeps firms operating in industries where they are no longer competitive.
D. it reduces the incentive for firms to invest in new technologies to maintain competitiveness.
A. the small fraction of workers losing jobs to international trade are no more deserving of assistance than others suffering job loss.
You might also like to view...
Consider the game depicted below. Player 1 decides between going L or R in stage 1 and 3 of the game. Player 2 decides between going l and r in stage 2 of the game.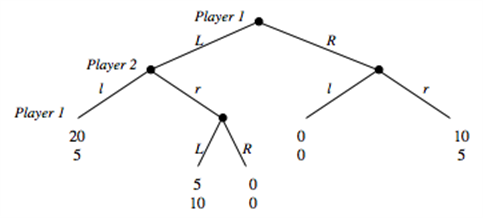
c. Identify the subgame perfect equilibrium strategies and outcome. d. Identify the Nash Equilibria that are not subgame perfect. e. For each Nash Equilibrium that is not subgame perfect, explain which parts of the Nash Equilibrium strategies are non-credible. f. Suppose you have developed a drug that can be administered without the victim being aware of it. The effect of the drug is that the victim suddenly becomes gullible and believes anything he is told. You only have 1 dose of the drug and decide to auction it off to the two players right before they play each other in the game you have analyzed so far. Each player is asked to submit a sealed bid, and the highest bidder will be sold the drug at a price equal to the highest bid. In case of a tie in bids, a coin is flipped to determine who wins and pays the price that was bid. Suppose in this part that payoffs are in terms of dollars and that bids can be made in one cent increments. Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay. Given that the players know each other's payoffs in the above game, what is the equilibrium price that you will be able to sell the drug for? (Hint: There are two possible answers.) g. In part (f), we said "Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay." Can you think of a Nash equilibrium to the auction that would end in a price of $8 if we had not made that statement in (f)? What will be an ideal response?
If two interdependent economies work independently pursuing the best interests of their own economies
A) both countries can end up worse than they planned because of international externalities. B) they will make other economies more vulnerable to international externalities. C) they will have to sacrifice their monetary autonomy to achieve their goals. D) both countries can end up worse than they planned because of the liquidity effect.
Which of the following is not true about marginal revenue product?
A. It shows the value of the marginal physical product. B. It is the marginal physical product times price of the product under perfect competition. C. It is the marginal physical product times marginal revenue. D. It shows the marginal costs of inputs.
The nominal rate of interest is 8.5 percent and the real rate is 5 percent. The expected rate of return on an investment is 8 percent. The firm should:
A. Not undertake the investment because the expected rate of return of 8 percent is less than the nominal interest rate B. Not undertake the investment because the expected rate of return of 8 percent is less than the nominal plus the real interest rate C. Undertake the investment because the expected rate of return of 8 percent is greater than the difference between the nominal and real interest rates D. Undertake the investment because the expected rate of return of 8 percent is greater than the real rate of interest