Equilibrium: A push of magnitude P acts on a box of weight W as shown in the figure. The push is directed at an angle ? below the horizontal, and the box remains a rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to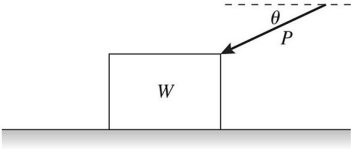
A. P sin ?.
B. P cos ?.
C. 0.
D. P cos ? + W.
E. P + W.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Young's Modulus: A piano wire has a radius of 0.50 mm. One end is fixed and the other is wrapped around a tuning peg, which has a diameter of 3.5 mm and is 80 cm away. After the wire just becomes taut, the peg is given three full turns. What is the tension in the wire? Young's modulus for steel is 2.0 × 1011 N/m2.
A. 3.8 kN B. 4.3 kN C. 6.5 kN D. 8.7 kN E. 9.8 kN
A box is pushed across a horizontal table at constant speed. Of the forces on it, which pair do we know are equal in magnitude because of Newton’s third law?
A. Normal force on the box and the weight of the box. B. Normal force on the box and the normal force on the table by the box. C. The force of kinetic friction on the box and the force applied to the box by the one pushing it. D. None of these are interaction pairs.
Conservation of angular momentum means that a spinning body tends to
A) fly apart. B) slow down. C) wobble into an eccentric orbit. D) gravitationally collapse. E) keep spinning.
Which of the following statements best describes the exclusion principle?
A) If a particle has a precisely defined position, it is excluded from having a precisely defined momentum. B) The laws of quantum mechanics are excluded from applying to large objects made of many atoms. C) Two fermions cannot occupy the same quantum state at the same time. D) Two photons cannot be in the same place at the same time. E) The laws of quantum mechanics are excluded from our common sense.