Critics of supply-side economics argue that
A. tax cuts do not affect supply, only demand.
B. supply-siders exaggerate the effects of tax cuts.
C. incentives have no effect on behavior.
D. the goals of supply-siders are not supported by most economists.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as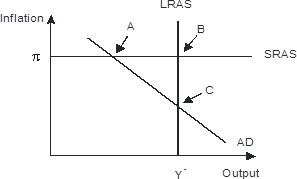
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
A classical IS—LM model of the world economy can be used to show that in a flexible exchange-rate system, a temporary increase in government purchases will cause
A) output and the real interest rate to rise, which reduces net exports but has an ambiguous effect on the real exchange rate. B) output and the real interest rate to rise, which increases net exports but has an ambiguous effect on the real exchange rate. C) output to rise and the real interest rate to fall, which reduces net exports and causes the exchange rate to depreciate. D) the real interest rate to fall, which causes the exchange rate to rise, which reduces net exports.
All of the following costs will vary depending on the geographic location of a firm's plant except which one?
A) land prices B) U.S. corporate taxes C) wages D) local taxes
When Pierre in Paris, France buys stock in Disney, Inc., he is contributing to:
A. capital outflow from the U.S. B. capital inflow to the U.S. C. domestic investment in the U.S. D. private savings in the U.S.