Which of the following is correct?
A. Vertical mergers are more likely to be acceptable under antitrust laws than are horizontal
mergers.
B. A vertical merger entails the merging of two or more competing firms.
C. Horizontal mergers are more likely to be acceptable under antitrust laws than are vertical
mergers.
D. Conglomerate mergers occur when two or more firms at various stages in a good's
production are combined.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 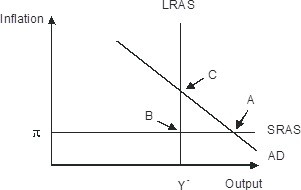
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C
Perfectly competitive industry X has constant costs and its product is an inferior good. The industry is currently in long-run equilibrium. The economy now goes into a recession and average incomes decline. The new long-run equilibrium will result in a(n)
A. decrease in output, but not in the equilibrium price of the product. B. increase in output and in the equilibrium price of the product. C. increase in output, but not in the equilibrium price of the product. D. decrease in output and in the equilibrium price of the product.
Adam Smith argued that each person in a competitive market is led to promote the
A) efficient use of society's resources, because each person's intention is to make society better off. B) efficient use of society's resources, even though it is no person's intention to make society better off. C) inefficient use of society's resources, even though each person's intention is to make society better off. D) inefficient use of society's resources, because it is no person's intention to make society better off.
Economic efficiency requires that a natural monopoly's price be
A) equal to average variable cost where it intersects the demand curve. B) equal to average total cost where it intersects the demand curve. C) equal to the lowest price the firm can charge and still make a normal profit. D) equal to marginal cost where it intersects the demand curve.