Sunk costs are:
A. costs that have been incurred and cannot be recovered.
B. explicit costs that will incur large implicit costs to recoup or recover.
C. costs that are upfront on a project and can be pulled out if the business goes under.
D. the cost of recovering lost expenditures.
A. costs that have been incurred and cannot be recovered.
You might also like to view...
In the diagrams below, the subscript "1" refers to the initial position of the curve, while the subscript "2" refers to the final position after the curve shifts.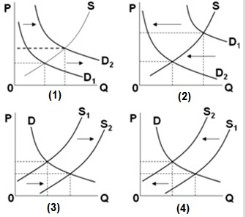 In which of the diagrams above would we see a shortage at the initial price after the indicated curve has shifted?
In which of the diagrams above would we see a shortage at the initial price after the indicated curve has shifted?
A. (1) and (4) B. (2) and (3) C. (1) and (3) D. (2) and (4)
What is the effect on the price and quantity of a product if both the demand and supply simultaneously increase?
What will be an ideal response?
The exchange rate between the dollar and the euro is
a. the price of European goods relative to U.S. goods. b. the price of U.S. goods relative to European goods. c. the number of euros you get for lending one dollar to a European for a year. d. the number of euros you get for one dollar.
Suppose a firm wants to expand sales of its product into a foreign country. Should the firm license local firms in the foreign country to use its technologies to produce the product or should it set up a foreign operation that it owns and controls? What factors should the firm consider in making the decision? When identifying these factors, clearly explain how and why they push the decision toward one or the other of the two available choices.
What will be an ideal response?