Velma, who is moving past you at a high rate of speed, holds a meter stick and a standard kilogram
Is it possible that your measurements could show the standard kilogram to have a mass of 2 kg while the meter stick still has its normal length of 1 m?
A) Yes, if Velma holds the meter stick parallel to its direction of motion.
B) Yes, if Velma holds the meter stick perpendicular to its direction of motion.
C) No, because mass actually decreases with velocity, rather than increasing.
D) No; if the kilogram's mass has increased to 2 kg, then it must be longer than 1 m.
E) No; if the kilogram's mass has increased to 2 kg, then it must be shorter than 1 m.
B
You might also like to view...
Circular Motion of Charges: In the figure, a small particle of charge -1.9 × 10-6 C and mass m = 3.1 × 10-12 kg has speed v0 = 8.1 × 103 m/s as it enters a region of uniform magnetic field. The particle is initially traveling perpendicular to the magnetic field and is observed to travel in the semicircular path shown with radius R = 5.0 cm. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field in the region. 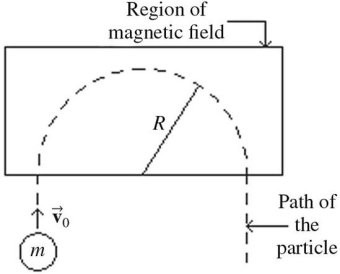
What will be an ideal response?
A fish appears to be 2.00 m below the surface of a pond when viewed almost directly above by a fisherman. What is the actual depth of the fish? (nwater = 1.33)
A) 2.66 m B) 0.67 m C) 1.5 m D) 0.38 m
A charge of 5.0 pC is distributed uniformly on a spherical surface (radius = 2.0 cm), and a second charge of ?2.0 pC is distributed uniformly on a concentric spherical surface (radius = 4.0 cm). Determine the magnitude of the electric field 3.0 cm from the center of the two surfaces
a. 30 N/C b. 50 N/C c. 40 N/C d. 20 N/C e. 70 N/C
As shown below, a square loop of wire of side a moves through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B perpendicular to the page at constant velocity
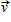 directed to the right. Which statement regarding the electric field induced in the wires is correct for the wires at the left and right sides of the loop?
directed to the right. Which statement regarding the electric field induced in the wires is correct for the wires at the left and right sides of the loop?
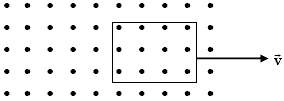
?
a.
The electric field 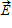 is directed upwards in both the right and left sides of the loop.
is directed upwards in both the right and left sides of the loop.
b.
The electric field 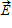 s directed upwards in the right side and downwards in the left side of the loop.
s directed upwards in the right side and downwards in the left side of the loop.
c.
The electric field 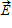 is directed upwards in the left side and downwards in the right side of the loop.
is directed upwards in the left side and downwards in the right side of the loop.
d.
The electric field 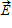 is directed downwards in both the right and left sides of the loop.
is directed downwards in both the right and left sides of the loop.
e.
There is no electric field present in any side of the loop.