In TILLING, a population of inbred organisms is mutagenized to saturation. DNA from mutagenized lines is isolated and amplified by PCR. PCR products are denatured and allowed to reanneal and then treated with an endonuclease
Why is the denaturation/re-annealing step important for the detection of mutant alleles?
Wild-type individuals in an M1 population will be homozygous and will produce a single PCR product. When wild-type PCR products reanneal after denaturation, all single strands have a perfect complement so the reanealed duplexes will contain no mismatches and will not be susceptible to nicking by the endonuclease. By contrast, mutants in an M1 population will be heterozygous, so there will be two different template DNAs – wild type and mutant – resulting in two different PCR products. When these PCR products reanneal after denaturation, they can form two different types of duplexes – homoduplexes (where both strands are either wild type or mutant) and heteroduplexes (where one strand is wild type and the other mutant). Heteroduplex strands will contain mismatches, which will be susceptible to nicking by the endonuclease. This differential sensitivity is detectable upon gel electrophoresis.
You might also like to view...
In rapidly dividing cells, expression of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes is the highest during the ____
a. mitosis to cytokinesis transition b. G1/S transition and into S phase c. G2/mitosis transition d. S/G2 transition e. metaphase to anaphase transition
We are currently in the
a. Archaean eon. b. Proterozoic eon. c. Paleozoic era. d. Mesozoic era. e. Cenozoic era.
In image "B" individuals within the population defend distinct territories for resources, resulting in a defined distance between each. This is an example of distribution.
Three population distribution patterns are shown in this figure.
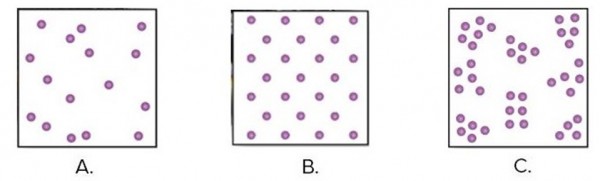
A. random
B. nonselected
C. clumped
D. forced
E. uniform
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
A. ventricles B. septa C. AV valves D. auricles E. atria