The figure above shows the demand curve for pizza
a. What is the marginal benefit of the 20th pizza?
b. What is the maximum price the consumer is willing to pay for the 20th pizza?
c. If the price of a pizza is $6, what is the consumer surplus of the 20th pizza?
d. If the price of a pizza is $10, what is the consumer surplus on all the pizzas consumed?
e. If the price of a pizza is $6, what is the consumer surplus on all the pizzas consumed?
a. The marginal benefit of the 20th pizza is $10.
b. The maximum price the consumer is willing to pay for the 20th pizza is $10.
c. If the price of a pizza is $6, the consumer surplus of the 20th pizza is $4.
d. If the price of a pizza is $10, the consumer surplus is $40.
e. If the price of a pizza is $6, the consumer surplus is $160.
You might also like to view...
The opportunity cost of an action: a. can be determined by considering the benefits that flow from the action as well as the monetary costs incurred as a result of the action. b. can be determined by adding up the bills incurred as a result of the action
c. can be objectively determined only by economists. d. is a subjective valuation that can be determined only by the individual who chooses the action.
Suppose the government imposes a tax of 10 percent on the first $40,000 of income and 20 percent on all income above $40,000 . What are the tax liability and the marginal tax rate for a person whose income is $50,000?
a. 12 percent and 20 percent, respectively b. 12 percent and $50,000 . respectively c. $6,000 and 12 percent, respectively d. $6,000 and 20 percent, respectively
The answer is: "It allows the inhabitants of a country to consume at a level beyond its production possibilities frontier." What is the question?
A) What do newly discovered resources do? B) What does technology do? C) What does specialization and international trade do? D) What does specialization do? E) a and b
If the dotted horizontal line represents the effect of a usury law then there is a ____ of loanable funds of _____ billion dollars.
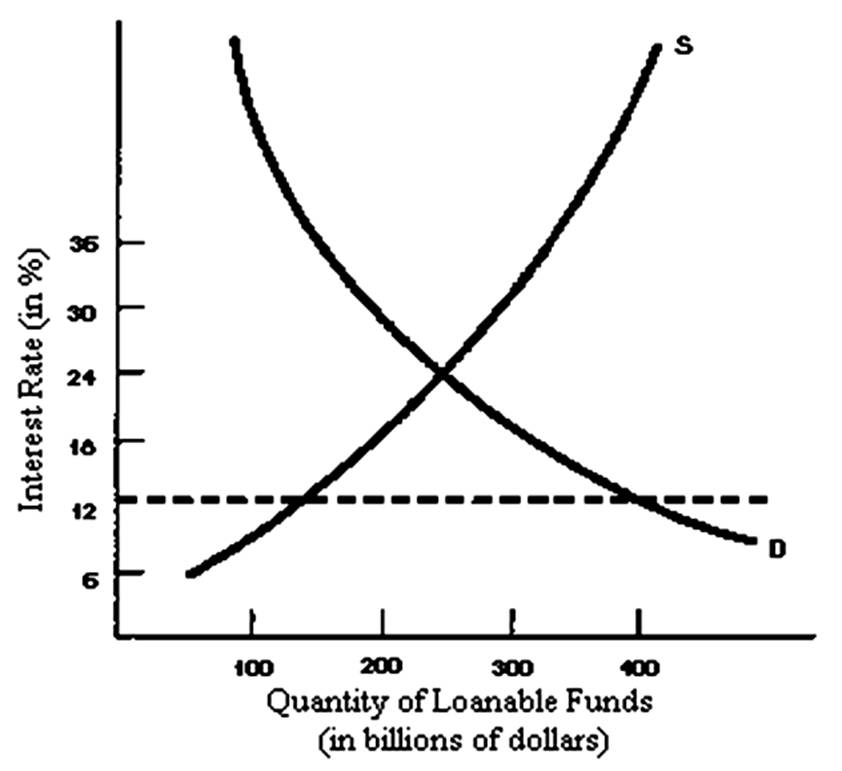
A. surplus; 275
B. shortage; 275
C. surplus; 400
D. shortage; 400