What is the role, if any, of aerosols in climate? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
They affect temperatures. The sulfate aerosols released by burning coal tend to
counteract the additional carbon dioxide emitted, though the presence of the aerosols is
fleeting (several weeks' residence time) and the presence of carbon dioxide lasting. As
pointed out on p. 373, GCMs that do not include aerosol effects fail to reproduce the correct
interhemispheric temperatures. Aerosols are connected to the cloudiness experienced. It is
thought that the presence of aerosols has led to increased cloudiness in the Northern
Hemisphere.
You might also like to view...
Irregulars typically have very few blue stars
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A bullet fired horizontally hits the ground in 0.5 s. If it had been fired with twice the velocity it would have hit the ground in
A) less than 0.5 s. B) more than 0.5 s. C) 0.5 s.
A U-238 nucleus (mass = 238 units) decays, transforming into an alpha particle (mass = 4.00 units) and a residual thorium nucleus (mass = 234 units). If the uranium nucleus was at rest, and the alpha particle has a speed of 1.50 × 10^7 m/s, determine the recoil speed of the thorium nucleus
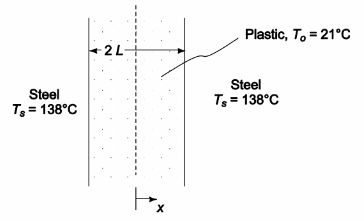
A 2.5-cm-thick sheet of plastic initially at 21°C is placed between two heated steel plates that are maintained at 138°C. The plastic is to be heated just long enough for its midplane temperature to reach 132°C. If the thermal conductivity of the plastic is 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K), the thermal diffusivity is 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s, and the thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible, calculate: (a) the required heating time, (b the temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued, and (c) the time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel plate.
GIVEN
• A sheet of plastic is placed between two heated steel plates
• Sheet thickness (2L) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Initial temperature (To) = 21°C
• Temperature of steel plates (Ts) = 138°C
• Heat until mid-plane temperature of sheet (Tc) = 132°C
• The thermal conductivity of the plastic (k) = 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K)
• The thermal diffusivity (?) = 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s
• The thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible
FIND
(a) The required heating time (b) The temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued (c) The time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel.
ASSUMPTIONS
• The initial temperature of the sheet is uniform
• The temperature of the steel plates is constant
• The thermal conductivity of the sheet is constant
SKETCH