In the analysis of the interest rate effect, when the price level changes, the quantity of money households and firms' want to hold and interest rates move in the ____ direction as the change in the price level, while investment and the quantity RGDP demanded move in the ____ direction as the change in the price level
a. Same, same
b. Same, opposite
c. Opposite, same
d. opposite, opposite
b
You might also like to view...
Assume a firm employs 10 workers and pays each $15 per hour. Further assume that the MP of the 10th worker is 5 units of output and that the price of the output is $4. According to economic theory, in the short run
A) the firm should hire additional workers. B) the firm should reduce the number of workers employed. C) the firm should continue to employ 10 workers. D) More information is required to answer this question.
Which of the following is not a principal means by which corporations obtain money for investment?
a. selling stocks b. selling bonds c. retaining earnings d. receiving dividends
Some of the nation's best minds are occupied with devising schemes to avoid taxes and to transfer income to favored groups at the expense of market efficiency. This is called _____
A) hedging. B) pork-barrel spending. C) rent seeking. D) skimming. E) profiteering.
Refer to the diagram and list of assumptions. If discrimination is ended:
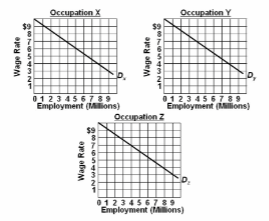
(1) the labor force is comprised of 9 million men and 9 million women workers;
(2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for labor; (3) men and women workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive, and workers seek to maximize their earnings.
A. men will leave occupations X and Y and enter occupation Z.
B. 4 million women will leave occupation Z, with 2 million entering occupation X and 2 million
entering occupation Y.
C. 3 million women will leave occupation Z, with 1.5 million entering occupation X and 1.5
million entering occupation Y.
D. 3 million women will leave occupation Z, all of whom will enter industry X.