AT&T is an example of a business that used market power to
A. avoid government regulation.
B. squash the competition.
C. invest in important research benefiting society.
D. minimize average costs of production.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix III. Which of the following is a property of this game?
Game Matrix III
The following questions refer to the game matrix below. Each firm has a choice of advertising, Ads, or not advertising, No ad. The profits each gets depend upon which it chooses.
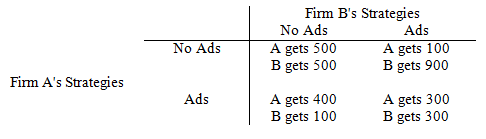
a. Both firms have dominant strategies.
b. There is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium.
c. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is Pareto optimal.
d. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is not Pareto optimal.
From the point of view of a particular country, capital outflows are:
A. purchases of domestic assets by foreigners. B. purchases of foreign goods or services by domestic households or firms. C. purchases of domestic goods or services by foreigners. D. purchases of foreign assets by domestic households or firms.
Suppose the long-run supply curve for a good is upward-sloping. The upward slope could be explained by
a. increases in production costs resulting from more firms coming into the market. b. a breakdown of the "free entry and exit" feature of competition. c. a breakdown of the "price taking" feature of competition. d. a stable demand curve for the good, that is, a demand curve that never shifts.
Suppose that Canada pegs its currency to the U.S. dollar at a rate of $C1 = $US1 and that Canada is a major exporter of crude oil to the United States. The increase in the price of oil that occurred in the second half of 2007 is likely to:
A) cause Canada to adopt a contractionary monetary policy and the United States to adopt an expansionary monetary policy. B) cause Canada to adopt an expansionary monetary policy and the United States to adopt a contractionary monetary policy. C) cause both Canada and the United States to adopt contractionary monetary policies. D) cause both Canada and the United States to adopt expansionary monetary policies.