Correcting a market with an externality through taxation is _________ correcting it through a quota.
A. more efficient than
B. less efficient than
C. just as efficient as
D. Any of these statements could be true depending on whether the tax is imposed on the buyer or seller.
A. more efficient than
You might also like to view...
Suppose a nation's saving, gross private domestic investment, government spending, and taxes remained unchanged from Year 1 to Year 2, but tariffs and quotas on imported goods and services rose by 20% from Year 1 to Year 2 . The net effect on the balance on goods and services would be:
a. It would have no effect on the balance on goods and services. b. It would make the balance on goods and services more positive. c. It would make the balance on goods and services more negative. d. There is no way to tell what effect it would have on the balance on goods and services.
A country has $50 million of domestic investment and net capital outflow of $15 million. What is saving?
a. $65 million b. -$65 million c. $35 million d. -$35 million
Assume that the real rate of interest is 5 percent and a lender charges a nominal interest rate of 15 percent. If a borrower expects that the rate of inflation next year will be 10 percent and the actual rate of inflation next year is 12 percent:
a. neither the borrower nor the lender benefits from inflation.
b. both the borrower and the lender lose from inflation.
c. the borrower benefits from inflation, while the lender loses from inflation.
d. the lender benefits from inflation, while the borrower loses from inflation.
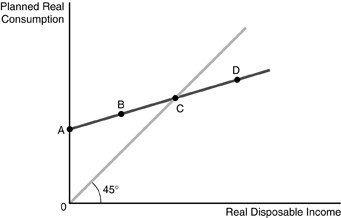 Refer to the above figure. The figure represents the consumption function for a consumer. Point C represents
Refer to the above figure. The figure represents the consumption function for a consumer. Point C represents
A. autonomous consumption. B. positive saving. C. negative saving. D. zero saving.