Explain the differences between asymmetric information, adverse selection, and moral hazard
What will be an ideal response?
Asymmetric information is a situation that occurs when one party to a transaction has more or better information than the other party has. Adverse selection is the tendency for the people who pose the greatest risks to insurers to buy insurance. Moral hazard is a change in behavior that occurs after a person becomes insured against a loss. Both adverse selection and moral hazard are a result of asymmetric information.
You might also like to view...
The Cost-Benefit Principle predicts that a person:
A. should take an action if its cost increases. B. is more likely to take an action if its cost increases. C. is more likely to take an action if its benefit increases. D. should take an action if its benefit increases.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 authorized investors to bring lawsuits against credit-rating agencies for a reckless failure to get the facts when providing a credit rating
This is an example of which remedy of conflicts of interest? A) regulate for transparency B) supervisory oversight C) leave it to the market D) socialization of information production
According to Milton Friedman, the reason there are two Phillips curves is because
A) the expected inflation rate is always higher than the actual inflation rate. B) wages are inflexible. C) prices are inflexible. D) the expected inflation rate does not instantaneously adjust to changes in the actual inflation rate. E) the expected inflation rate is equal to 1 minus the actual inflation rate.
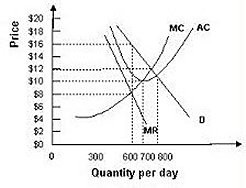 For the monopoly in the above figure, if the firm is currently producing 700 units, which of the following is correct?
For the monopoly in the above figure, if the firm is currently producing 700 units, which of the following is correct?
A. It is maximizing its profits. B. It is incurring a loss. C. It could earn higher profits if it produced more units each day. D. It could earn higher profits if it produced fewer units each day.